PSAIM Services
PROCESS SAFETY & ASSET INTEGRITY MANAGEMENTINTRODUCTION TO AIMS
Asset Integrity Management System (AIMS) includes several activities such as planning, control and monitoring activities, to exploit opportunities and to reduce risks.
The goal is to make sure that a system is in place to maintain asset integrity when needed, throughout the entire life cycle. Control measures include personnel, physical resources, procedures, process control systems and emergency plans dedicated to this task (NOPSEMA, 2012).
Asset Integrity processes are fundamental in reducing company risks: developed in industries with reduced or volatile margins, they should be now implemented anywhere a correct management is quintessential for company reputation, business continuity and efficiency or in all cases where the ageing of equipment can become a critical issue.
The challenge is to find a balance between the high operating performances required by assets, on one hand, and the costs of TIMS activities (Testing, Inspection, Maintenance and Substitution), on the other; the system should be flexible enough to follow market evolution, while maintaining high safety and environmental standards. International recommended practices (API 581, 2008) can help an organization develop an inspection plan based on the risk posed by each equipment. Others may prefer a more holistic approach and develop their own system.
DEFINITION
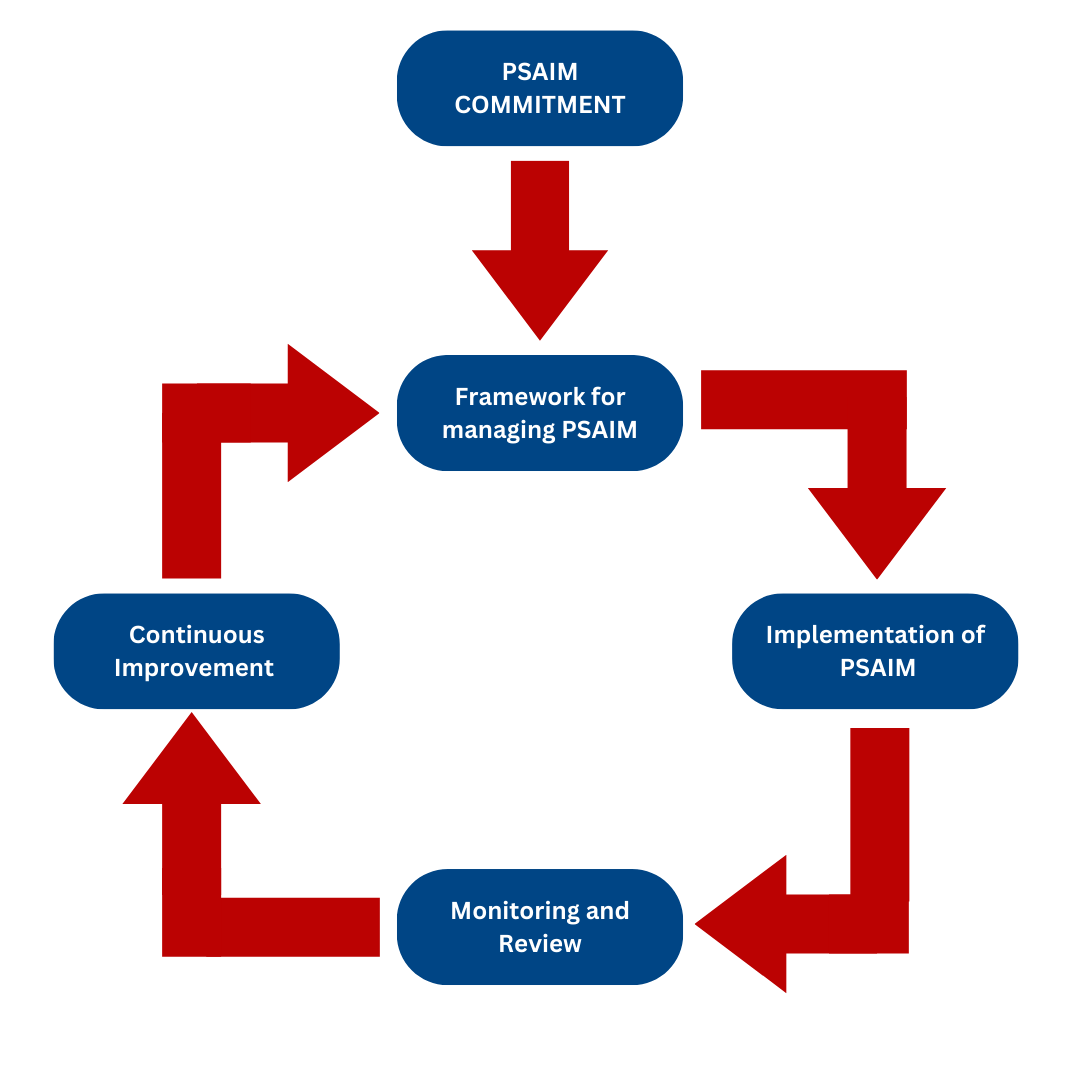
PSAIM Is the ability to manage risks and assure the integrity of assets throughout their life cycle.
PSAIM can be an effective tool for increasing not only the safety of an operation, but its efficiency, cost-effectiveness and quality as well. Continuous improvement management cycle: Plan, Do, Check, Act is the most management systems to prevent the MAE.
- Plan – Development of a policy and plans for implementation.
- Do – Implementation and execution of the plan with adequate resources.
- Check – Review and measurement of performance.
- Action – Taking action to act on deviations identified and lessons learned
PSAIM DEVELOPMENT
The activities for PSAIM Development include the following:
- Document / System Review
- Development / revise of PSAIM System Framework
- Development / revise of PSAIM System Procedures
The step of this work is to review and develop / revise the amount of documents and procedure which are not well develop and could only be determined upon the completion of the audit PSAIM phase.
Benefit of AIMS
Implementing an AIMS approach provides several advantages:
- Reduce the probability of catastrophic events;
- Limit the exposure to risk, in terms of health, safety, environment, reputation and business continuity;
- Help the Companies’ turnaround from “maintenance after fault”, reacting to events, to preventive and predictive maintenance schemes that proactively prevent faults
PSAIM IMPLEMENTATION
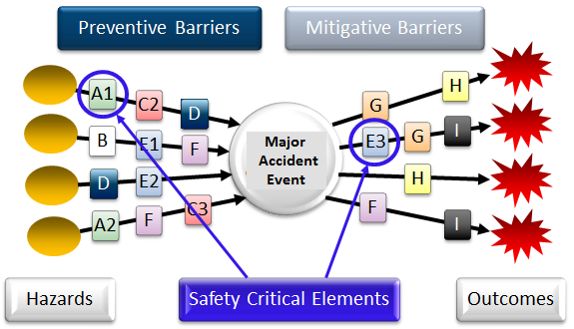
The purpose is to establish and maintain barriers so that the risk faced at any given time can be handled by preventing an undesirable incident from occurring or by limiting the consequences should such an incident occur.
The gap that found during audit from Integrity, Reliability & Process Safety Assessment phase BV will provide the following activities to support the life cycle of PSAIM
- Following up on actions from PSAIM audits or gap assessments.
- Facilitation of process hazard analysis such as HAZID, HAZOP / REHAZOP and SIL LOPA
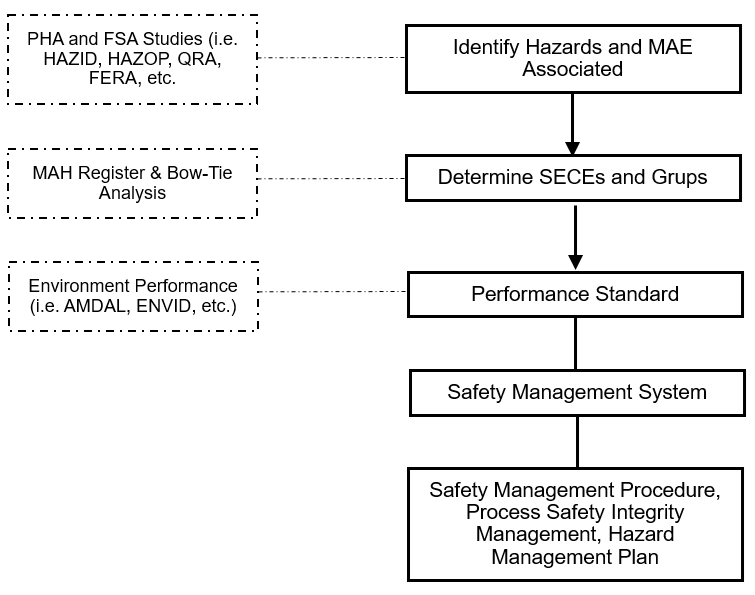
- Identification of MAH, SECE
- Implementation of Asset Integrity, Barrier Management, Reliability & Process Safety Assessment,
MOC - Integration of PSAIM software
- Updating, communication and training of PSAIM-related procedures.
- Other PSAIM related programmers.
Assign PSAIM Champion
Appoint a Champion or person in charge of PSAIM and its organization and give authority to competent personnel.
PSAIM Policy & Program
Conduct Gap Assessment, Develop policies, Roadmap, Plans/programs for PSAIM implementation.
PSAIM Socialization & Coordination
Carry out socialization and routine coordination regarding progress of PSAIM the implementation with related personnel and functions/departments.
Conduct Major Accident Study
Identify and Assess Major Accident Hazards related to the hazards contained in operational activities.
Process Safety Barrier & SECE Management
Identifying Process Safety barriers needed and available at process facilities and managing Safety & Environmental Critical Elements to prevent Major Accidents.
Assurance & Monitoring
Carry out PSAIM audits to ensure compliance with PSAIM management

PREVENTION MAJOR ACCIDENT

BARRIER PERFORMANCE DAPAT DIPANTAU DENGAN MELAKUKAN
MONITORING PROCESS SAFETY EVENT INDICATOR
The dashboard addresses all key aspects of the Policy:
- Plant: Maintenance, Inspection, Testing
- Processes : Monitoring critical safety processes, audit action plans
- People : Management leadership, training